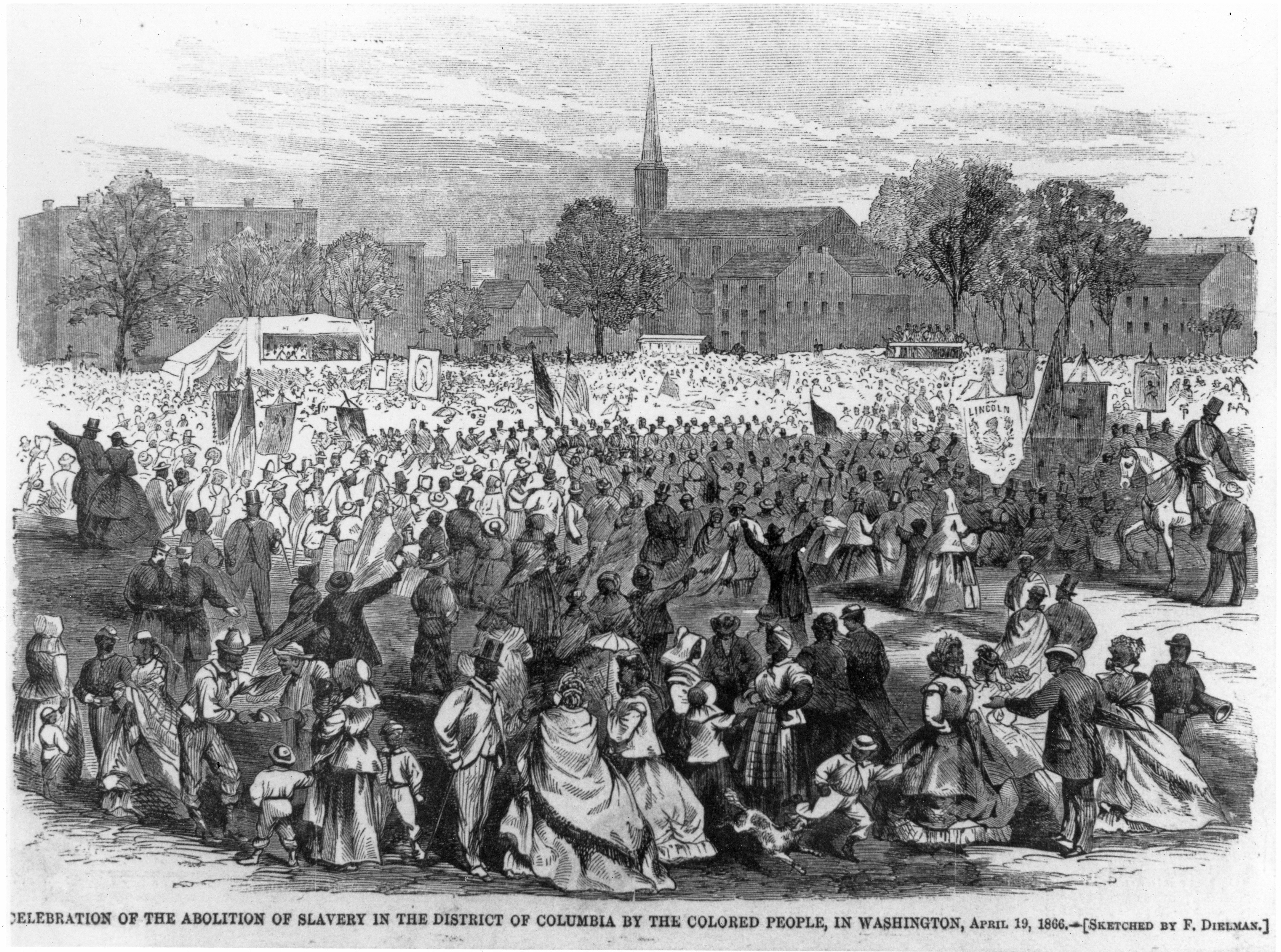Slavery is one of the darkest chapters in human history, and understanding its abolition is crucial for acknowledging progress and challenges in human rights. The question, "how many years ago did slavery get abolished," brings us to a pivotal moment in history that reshaped societies worldwide. This article explores the timeline, key events, and lasting impacts of slavery's abolition.
Slavery's abolition marked a significant turning point in global history. It signified the end of an era where human beings were treated as property. This period brought about monumental changes in social structures, economies, and legal systems, influencing the trajectory of modern civilization.
Join us as we delve into the intricate history of slavery's abolition, examining the critical milestones, influential figures, and the enduring legacies that continue to shape contemporary discussions about equality and justice.
Read also:Comprehensive Guide To Chase Com Banking Help Your Ultimate Resource
Table of Contents
- Timeline of Slavery Abolition
- Global Impact of Slavery Abolition
- Key Figures in the Abolition Movement
- Legal Framework and Legislation
- Economic Effects of Slavery Abolition
- Social Changes Post-Abolition
- Resistance and Challenges
- Modern-Day Slavery
- Education and Awareness
- Conclusion
Timeline of Slavery Abolition
How Many Years Ago Did Slavery Get Abolished?
The abolition of slavery occurred at different times across the world, depending on the region and its socio-political context. In the United States, slavery was officially abolished with the ratification of the 13th Amendment on December 6, 1865. As of 2023, this means slavery was abolished approximately 158 years ago in the U.S.
However, the timeline varies globally. For instance, the British Empire abolished slavery in 1833, while Brazil, the last country in the Americas to abolish slavery, did so in 1888. These timelines highlight the complexity of ending an institution deeply embedded in various societies.
Key dates include:
- 1807: The British Parliament passes the Slave Trade Act, prohibiting the trade of enslaved people.
- 1833: The Slavery Abolition Act is passed in the British Empire, ending slavery in most of its colonies.
- 1865: The 13th Amendment abolishes slavery in the United States.
- 1888: Brazil abolishes slavery with the Golden Law.
Global Impact of Slavery Abolition
Transforming Societies Worldwide
Abolishing slavery had profound effects on societies around the world. Economically, the shift from slave-based labor to wage labor systems disrupted traditional industries, particularly agriculture. Socially, the abolition movement laid the groundwork for civil rights and equality movements.
However, the transition was not immediate or seamless. Many former slaves faced significant challenges, including poverty, discrimination, and lack of access to education and resources. These issues persisted for generations, contributing to systemic inequalities that continue to affect marginalized communities today.
Key Figures in the Abolition Movement
Influential Leaders Who Shaped History
The abolition of slavery was driven by courageous individuals who risked their lives to fight for justice. Prominent figures include:
Read also:The Randy Watson Experience A Comprehensive Exploration Of His Journey Legacy And Impact
- William Wilberforce: A British politician who played a pivotal role in ending the transatlantic slave trade.
- Harriet Tubman: An American abolitionist and former slave who helped hundreds escape through the Underground Railroad.
- Frederick Douglass: A former slave turned influential orator and writer, advocating for abolition and civil rights.
These leaders, among others, inspired global movements that challenged the moral and ethical foundations of slavery.
Legal Framework and Legislation
The Role of Laws in Ending Slavery
Legislation was instrumental in abolishing slavery. In the United States, the Emancipation Proclamation, issued by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863, declared the freedom of enslaved people in Confederate states. However, it was the 13th Amendment that officially ended slavery nationwide.
Globally, countries enacted laws to dismantle slavery's legal structures. The Slavery Abolition Act in the British Empire set a precedent for other nations to follow. These legal frameworks not only abolished slavery but also established protections for formerly enslaved individuals.
Economic Effects of Slavery Abolition
Shifting Economies Post-Abolition
The end of slavery forced economies reliant on slave labor to adapt. Plantations in the Southern United States, for example, struggled to transition to wage labor systems, leading to economic instability. In contrast, industrialized regions experienced growth as they embraced new labor models.
Despite these challenges, the abolition of slavery paved the way for economic diversification and innovation. It also highlighted the moral and economic costs of exploitation, prompting nations to invest in more equitable systems.
Social Changes Post-Abolition
Building New Societies
Post-abolition, societies faced the monumental task of rebuilding and reintegrating former slaves. This period saw the emergence of new social structures, including educational institutions and civil rights organizations. However, systemic racism and inequality persisted, requiring ongoing efforts to achieve true equality.
Education played a crucial role in empowering formerly enslaved individuals. Initiatives like the Freedmen's Bureau in the United States provided resources for education, healthcare, and employment, helping to create a more inclusive society.
Resistance and Challenges
Opposition to Abolition
Despite widespread support for abolition, resistance was significant. Pro-slavery factions argued that slavery was essential for economic stability and cultural identity. This resistance manifested in political debates, violent conflicts, and attempts to undermine abolitionist efforts.
In the United States, the Civil War (1861-1865) was a direct result of these tensions. The war ultimately led to the abolition of slavery but at a tremendous cost in lives and resources. Globally, similar conflicts and debates underscored the deep-rooted nature of slavery's legacy.
Modern-Day Slavery
Continuing the Fight Against Exploitation
Although legal slavery was abolished centuries ago, modern-day slavery persists in various forms, including human trafficking, forced labor, and child exploitation. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), approximately 25 million people are victims of forced labor globally.
Efforts to combat modern slavery focus on strengthening legal frameworks, raising awareness, and empowering vulnerable communities. Organizations like the United Nations and NGOs play critical roles in addressing this ongoing issue.
Education and Awareness
Learning from the Past to Shape the Future
Education is essential in understanding the history of slavery and its abolition. By studying this period, we gain insights into the struggles and triumphs of those who fought for freedom. Schools, museums, and cultural institutions worldwide offer resources to educate future generations about this important chapter in history.
Raising awareness also involves acknowledging the lasting impacts of slavery on contemporary societies. This includes addressing systemic racism, promoting equality, and supporting marginalized communities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question, "how many years ago did slavery get abolished," leads us to reflect on the profound changes that reshaped societies worldwide. From the United States to the British Empire and beyond, the abolition of slavery marked a turning point in human history. However, the fight for equality and justice continues, as modern-day slavery and systemic inequalities persist.
We invite you to join the conversation by sharing your thoughts and insights in the comments below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of this critical topic. Together, we can honor the legacy of those who fought for freedom and work towards a more just and equitable world.
References:
- International Labour Organization. (2022). Global Estimates of Modern Slavery.
- United Nations. (2023). Human Rights and the Abolition of Slavery.
- Encyclopedia Britannica. (2023). Slavery Abolition Act.