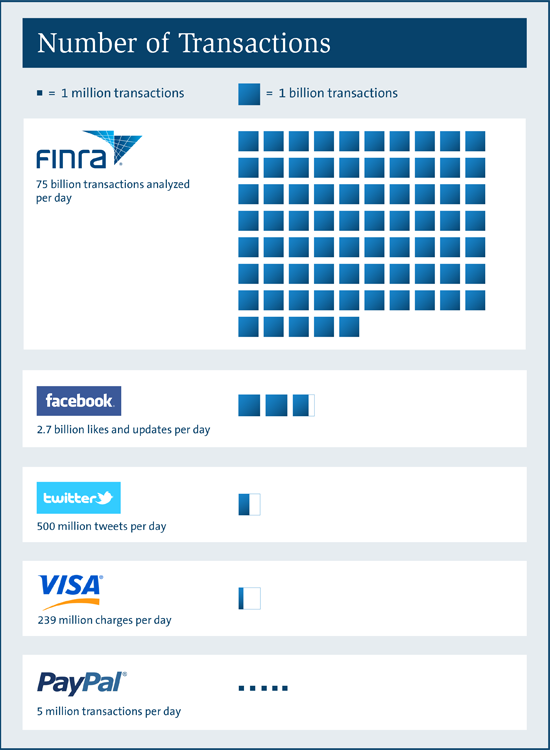
Understanding the role of regulatory bodies in the financial sector is crucial for investors, brokers, and financial professionals alike. One of the most significant organizations in the United States is the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, commonly known as FINRA. FINRA plays a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity of the financial markets and protecting investors from fraudulent activities. In this article, we will delve into the details of what FINRA is, its functions, and why it matters to you.
As a self-regulatory organization (SRO), FINRA operates under the oversight of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). It enforces rules and regulations that govern broker-dealers and securities firms, ensuring fair practices and transparency in the financial industry. Whether you're an investor looking to safeguard your assets or a professional seeking compliance guidelines, understanding FINRA is essential.
This article provides an in-depth exploration of FINRA's structure, responsibilities, and the impact it has on the financial markets. We will also discuss its historical background, key functions, and how it contributes to maintaining trust in the financial system. By the end of this guide, you will have a clear understanding of why FINRA is a cornerstone of the U.S. financial regulatory framework.
Read also:What Is An Aba Number In Banking A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction to FINRA
- History and Background of FINRA
- Structure and Governance of FINRA
- Key Functions of FINRA
- FINRA's Regulatory Authority
- Enforcement Actions and Penalties
- Investor Protection Initiatives
- Challenges Facing FINRA
- The Future of FINRA
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to FINRA
Understanding the Role of FINRA
FINRA stands as one of the largest independent regulators for securities firms doing business in the United States. Established in 2007 through the consolidation of the National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD) and the New York Stock Exchange's (NYSE) member regulation, enforcement, and arbitration functions, FINRA serves as a watchdog for the financial industry.
FINRA operates under the principle of protecting investors while maintaining the integrity of the securities markets. It achieves this by enforcing rules that govern broker-dealers and ensuring compliance with federal securities laws. With over 3,500 employees across the U.S., FINRA plays a vital role in overseeing the activities of securities firms and their registered representatives.
History and Background of FINRA
The Evolution of FINRA
The origins of FINRA can be traced back to the formation of the National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD) in 1939. The NASD was established to promote ethical practices and fair competition among securities firms. Over the years, the NASD expanded its regulatory functions, eventually merging with the NYSE's regulatory operations to form FINRA in 2007.
This merger aimed to streamline regulatory processes and create a more efficient and effective oversight mechanism for the financial industry. By consolidating the regulatory functions of two major organizations, FINRA became a unified authority responsible for enforcing rules and protecting investors.
Structure and Governance of FINRA
How FINRA is Organized
FINRA operates under a unique governance structure that ensures transparency and accountability. Its board of governors consists of both industry and independent members, ensuring a balanced approach to rule-making and enforcement. The organization is funded through fees assessed on securities firms, which helps maintain its independence from government funding.
Within FINRA, various departments focus on specific areas such as market regulation, enforcement, and investor education. This division of responsibilities allows FINRA to address the diverse needs of the financial industry and adapt to evolving challenges.
Read also:Two And A Half Men A Comprehensive Guide To The Iconic Tv Series
Key Functions of FINRA
What FINRA Does
FINRA performs several critical functions to uphold the integrity of the financial markets. These include:
- Regulation of Broker-Dealers: FINRA oversees the activities of securities firms and their registered representatives, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
- Enforcement of Rules: FINRA enforces rules related to sales practices, trading activities, and financial responsibilities of broker-dealers.
- Arbitration and Mediation: FINRA provides a forum for resolving disputes between investors and securities firms through arbitration and mediation processes.
- Investor Education: FINRA offers resources and tools to help investors make informed decisions and understand the risks associated with investing.
FINRA's Regulatory Authority
The Scope of FINRA's Power
FINRA's regulatory authority extends to nearly all aspects of the securities industry. It has the power to conduct investigations, impose fines, and suspend or bar individuals and firms that violate its rules. Additionally, FINRA collaborates with other regulatory agencies, such as the SEC, to address cross-border issues and enhance market oversight.
By maintaining a robust regulatory framework, FINRA ensures that securities firms operate in a fair and transparent manner. This, in turn, fosters trust and confidence among investors, which is essential for the functioning of the financial markets.
Enforcement Actions and Penalties
How FINRA Enforces Compliance
FINRA takes a proactive approach to enforcing compliance with its rules. It conducts regular examinations of securities firms to identify potential violations and addresses these through a range of enforcement actions. These actions may include:
- Issuing fines and penalties
- Suspending or barring individuals and firms
- Requiring remedial actions to address deficiencies
FINRA's enforcement efforts are supported by advanced data analytics and surveillance tools that enable it to detect suspicious activities and respond promptly. This commitment to enforcement helps deter misconduct and promotes ethical behavior in the financial industry.
Investor Protection Initiatives
FINRA's Commitment to Safeguarding Investors
Investor protection is at the core of FINRA's mission. The organization offers a range of resources and tools to help investors make informed decisions and avoid fraudulent schemes. These include:
- BrokerCheck: A free tool that allows investors to research the background and registration status of securities firms and their representatives.
- Investor Alerts: Regular updates on emerging risks and scams in the financial markets.
- Education Programs: Workshops and online courses designed to enhance investors' financial literacy.
By empowering investors with knowledge and resources, FINRA plays a crucial role in protecting them from fraudulent activities and ensuring fair treatment in the financial markets.
Challenges Facing FINRA
Addressing Evolving Regulatory Needs
Like any regulatory body, FINRA faces challenges in adapting to the rapidly changing landscape of the financial industry. Some of the key challenges include:
- Technological Advancements: Keeping pace with innovations in fintech and digital assets while ensuring proper oversight.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Protecting sensitive investor information from cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Globalization: Addressing cross-border issues and collaborating with international regulatory bodies.
FINRA continues to evolve its strategies and tools to meet these challenges and maintain its effectiveness as a regulatory authority.
The Future of FINRA
Innovations and Adaptations
Looking ahead, FINRA is poised to play an even more critical role in shaping the future of the financial industry. By embracing new technologies and fostering collaboration with other regulatory bodies, FINRA aims to enhance its capabilities and address emerging risks.
Key areas of focus for FINRA in the future include expanding its use of artificial intelligence and machine learning for surveillance, enhancing its investor protection initiatives, and promoting diversity and inclusion within the financial industry. These efforts will ensure that FINRA remains a leader in regulatory innovation and investor protection.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, FINRA is a vital component of the U.S. financial regulatory framework, dedicated to protecting investors and maintaining the integrity of the securities markets. Its comprehensive approach to regulation, enforcement, and investor education makes it an indispensable organization in the financial industry.
We encourage readers to explore FINRA's resources and stay informed about developments in the financial markets. By doing so, you can make better-informed decisions and protect your investments. Please feel free to leave your thoughts and questions in the comments section below, and don't hesitate to share this article with others who may benefit from it. Together, we can promote a more transparent and trustworthy financial system.
For further reading, consider exploring related articles on our site that delve into specific aspects of FINRA's operations and the broader financial regulatory landscape.
Data Sources: